Using GitLab CI/CD with a Bitbucket Cloud repository
DETAILS: Tier: Premium, Ultimate Offering: GitLab.com, Self-managed, GitLab Dedicated
GitLab CI/CD can be used with Bitbucket Cloud by:
- Creating a CI/CD project.
- Connecting your Git repository by URL.
To use GitLab CI/CD with a Bitbucket Cloud repository:
-
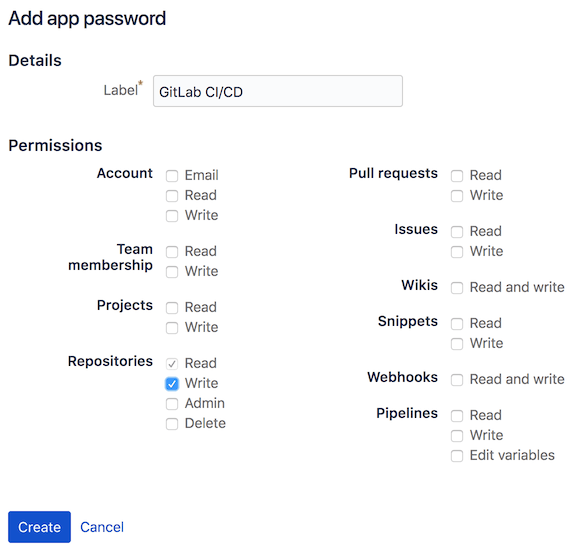
In Bitbucket, create an App password to authenticate the script that sets commit build statuses in Bitbucket. Repository write permissions are required.
-
In Bitbucket, from your repository, select Clone, then copy the URL that starts after
git clone. -
In GitLab, create a project:
- On the left sidebar, at the top, select Create new ({plus}) and New project/repository.
- Select Run CI/CD for external repository.
- Select Repository by URL.
- Complete the fields:
- For Git repository URL, enter the URL of your Bitbucket repository. Make sure to remove your
@username. - For Username, enter the username associated with the App password.
- For Password, enter the App password from Bitbucket.
- For Git repository URL, enter the URL of your Bitbucket repository. Make sure to remove your
GitLab imports the repository and enables Pull Mirroring. You can check that mirroring is working in the project in Settings > Repository > Mirroring repositories.
-
In GitLab, create a personal access token with
apiscope. The token is used to authenticate requests from the web hook that is created in Bitbucket to notify GitLab of new commits. -
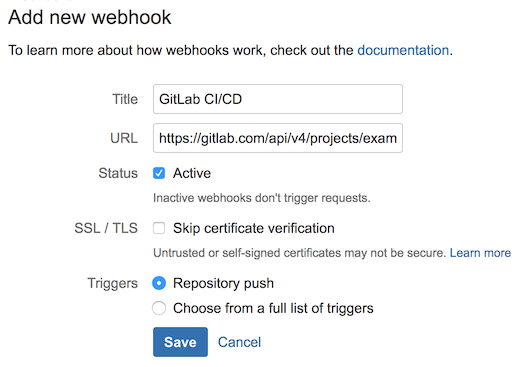
In Bitbucket, from Settings > Webhooks, create a new webhook to notify GitLab of new commits.
The webhook URL should be set to the GitLab API to trigger pull mirroring, using the personal access token we just generated for authentication.
https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/projects/:project_id/mirror/pull?private_token=<your_personal_access_token>The webhook trigger should be set to Repository Push.
After saving, test the webhook by pushing a change to your Bitbucket repository.
-
In GitLab, from Settings > CI/CD > Variables, add variables to allow communication with Bitbucket through the Bitbucket API:
-
BITBUCKET_ACCESS_TOKEN: The Bitbucket app password created above. This variable should be masked. -
BITBUCKET_USERNAME: The username of the Bitbucket account. -
BITBUCKET_NAMESPACE: Set this variable if your GitLab and Bitbucket namespaces differ. -
BITBUCKET_REPOSITORY: Set this variable if your GitLab and Bitbucket project names differ.
-
-
In Bitbucket, add a script that pushes the pipeline status to Bitbucket. The script is created in Bitbucket, but the mirroring process copies it to the GitLab mirror. The GitLab CI/CD pipeline runs the script, and pushes the status back to Bitbucket.
Create a file
build_statusand insert the script below and runchmod +x build_statusin your terminal to make the script executable.#!/usr/bin/env bash # Push GitLab CI/CD build status to Bitbucket Cloud if [ -z "$BITBUCKET_ACCESS_TOKEN" ]; then echo "ERROR: BITBUCKET_ACCESS_TOKEN is not set" exit 1 fi if [ -z "$BITBUCKET_USERNAME" ]; then echo "ERROR: BITBUCKET_USERNAME is not set" exit 1 fi if [ -z "$BITBUCKET_NAMESPACE" ]; then echo "Setting BITBUCKET_NAMESPACE to $CI_PROJECT_NAMESPACE" BITBUCKET_NAMESPACE=$CI_PROJECT_NAMESPACE fi if [ -z "$BITBUCKET_REPOSITORY" ]; then echo "Setting BITBUCKET_REPOSITORY to $CI_PROJECT_NAME" BITBUCKET_REPOSITORY=$CI_PROJECT_NAME fi BITBUCKET_API_ROOT="https://api.bitbucket.org/2.0" BITBUCKET_STATUS_API="$BITBUCKET_API_ROOT/repositories/$BITBUCKET_NAMESPACE/$BITBUCKET_REPOSITORY/commit/$CI_COMMIT_SHA/statuses/build" BITBUCKET_KEY="ci/gitlab-ci/$CI_JOB_NAME" case "$BUILD_STATUS" in running) BITBUCKET_STATE="INPROGRESS" BITBUCKET_DESCRIPTION="The build is running!" ;; passed) BITBUCKET_STATE="SUCCESSFUL" BITBUCKET_DESCRIPTION="The build passed!" ;; failed) BITBUCKET_STATE="FAILED" BITBUCKET_DESCRIPTION="The build failed." ;; esac echo "Pushing status to $BITBUCKET_STATUS_API..." curl --request POST "$BITBUCKET_STATUS_API" \ --user $BITBUCKET_USERNAME:$BITBUCKET_ACCESS_TOKEN \ --header "Content-Type:application/json" \ --silent \ --data "{ \"state\": \"$BITBUCKET_STATE\", \"key\": \"$BITBUCKET_KEY\", \"description\": \"$BITBUCKET_DESCRIPTION\",\"url\": \"$CI_PROJECT_URL/-/jobs/$CI_JOB_ID\" }" -
In Bitbucket, create a
.gitlab-ci.ymlfile to use the script to push pipeline success and failures to Bitbucket. Similar to the script added above, this file is copied to the GitLab repository as part of the mirroring process.stages: - test - ci_status unit-tests: script: - echo "Success. Add your tests!" success: stage: ci_status before_script: - "" after_script: - "" script: - BUILD_STATUS=passed BUILD_KEY=push ./build_status when: on_success failure: stage: ci_status before_script: - "" after_script: - "" script: - BUILD_STATUS=failed BUILD_KEY=push ./build_status when: on_failure
GitLab is now configured to mirror changes from Bitbucket, run CI/CD pipelines
configured in .gitlab-ci.yml and push the status to Bitbucket.